Boeing 787 Power Analysis - Innovations in Distribution and Protection - SSPC [Wickway]
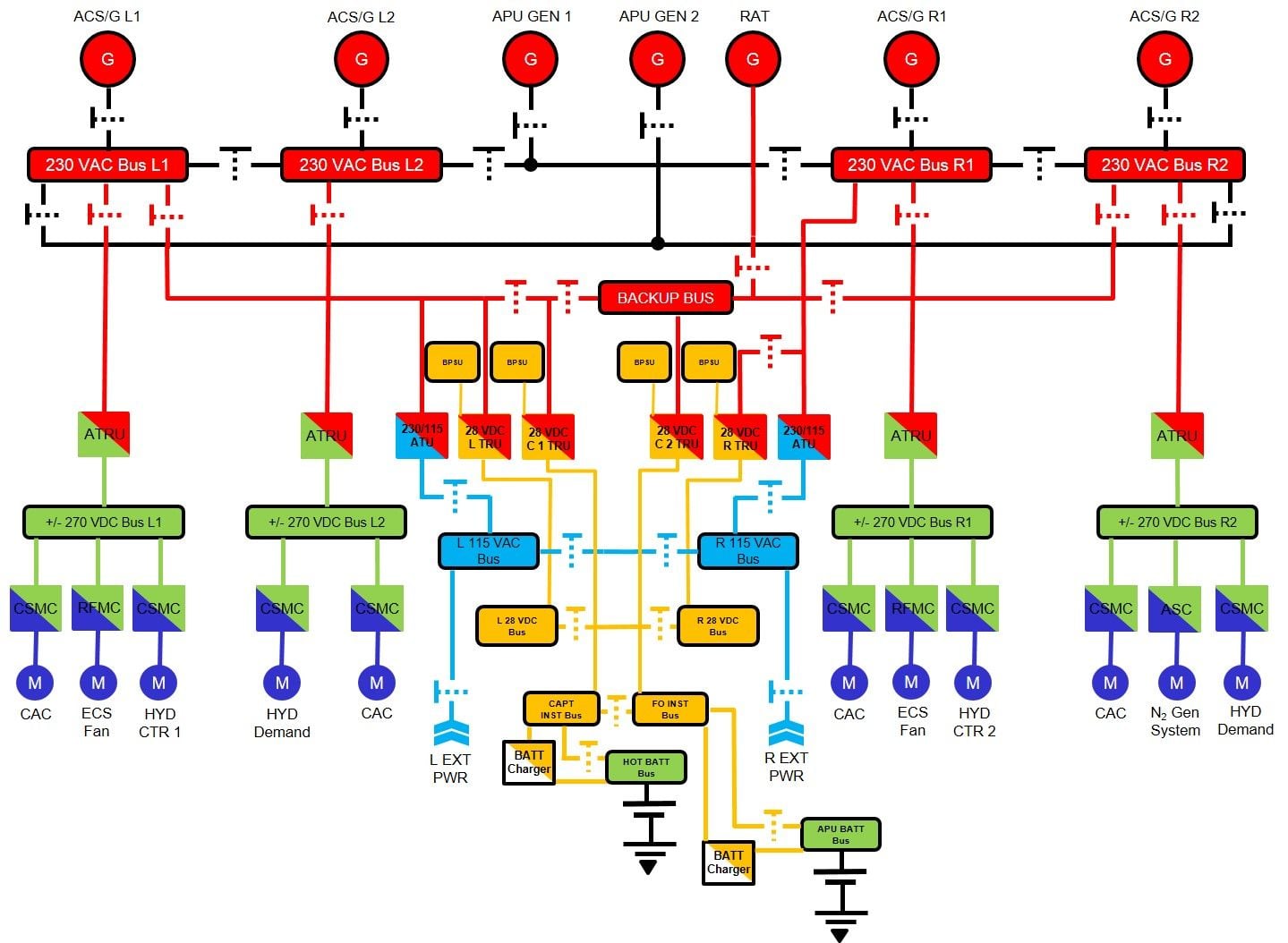
The electrical system used in the Boeing 787 is a hybrid voltage system consisting of the following types of voltages: 235 volts alternating current (VAC), 115 VAC, 28 volts direct current (VDC), and ± 270 VDC. When we analyze the power supply of the Boeing 787, we will find that this system is an innovation in power distribution and protection. The traditional 115 VAC and 28 VDC voltage types, while the 235 VAC and ± 270 VDC voltage types are the result of a leak free electrical structure, which leads to a significant expansion of the electrical system and generates twice as much electricity as previous Boeing aircraft models. The system consists of six generators, two for each engine and two for each APU, operating at 235 VAC to reduce the weight of the generator branch lines. The system also includes ground power sockets for repairing aircraft on the ground without using APU.
The generator is directly connected to the engine gearbox and therefore operates at a variable frequency (360 to 800 Hz) proportional to the engine speed. This type of generator is the simplest and most effective method of power generation because it does not include complex constant speed drives, which are key components of integrated drive generators (IDGs). As a result, compared to traditional IDG, it is expected that the generator will be more reliable, require less maintenance, and have lower backup costs.
The electrical system has two electrical/electronic (E/E) brackets, one forward and one backward, as well as many remote power distribution units (RPDUs) used to support aircraft electrical equipment. The system reduces weight by reducing the size of the feeder lines. The rear E/E bracket provides a limited number of 235.VAC electrical equipment, while the forward E/E bracket and RPDU support most aircraft electrical equipment at 115 VAC or 28 VDC, as shown in Figure 3 RPDU is mainly based on solid-state power controllers (SSPCs), rather than traditional thermal circuit breakers and relays. The ± 270 VDC system is provided by four automatic transformer rectifier units, which convert 235 VAC power to ± 270 VDC. The ± 270 VDC system supports a small number of large adjustable speed motors required for emission free architecture. These include cabin booster compressor motors, ram air fan motors, nitrogen generation system compressors for fuel tank inerting, and large hydraulic pump motors.
As shown in the figure, the system has two forward facing 115 VAC external power sockets, which can provide service to the aircraft on the ground without using APU; It also has two backward 115 VAC external power sockets for maintenance activities that require the operation of large adjustable speed motors.